A fancy blue diamond fascinates collectors with their boron-induced hue and unmatched rarity.
Rare natural blue diamonds command record prices at top-tier auction houses worldwide.
GIA 1.09 Carat Pear Diamond Fancy Blue IF Clarity |

|
| Click on the Image |
Table Of Contents
- 1) What Is A Blue Diamond?
- 2) Blue Diamond Color Grading And Classification
- 3) Natural Vs Treated And Synthetic Blue Diamonds
- 4) Where Do Blue Diamonds Come From?
- 5) Blue Diamond Pricing And Value Factors
- 6) Blue Diamond Jewelry: Styles, Trends, And Demand
- 7) How To Identify And Buy A Real Blue Diamond
- 8) Most Famous Blue Diamonds In The World
|
|
1) What Is A Blue Diamond?Back To Top |
Blue diamonds are among the rarest and most mesmerizing natural diamonds in the world. Their rich blue color, caused by trace elements like boron, makes them highly sought-after by collectors and investors. Unlike common diamonds, these rare stones combine geological wonder with luxury appeal.
|
|
1.a) The Meaning Behind Blue DiamondsBack To Top |
Blue diamonds symbolize rarity, power, and quiet confidence. Their deep hues evoke calmness, stability, and trust—traits often associated with loyalty and royalty. As demand rises, these natural fancy color diamonds have become prized heirlooms and modern investment assets.
Natural Formation And Color Origin
Blue diamonds form deep inside the Earth under intense heat and pressure, just like all diamonds. What sets them apart is the trace amount of boron trapped inside their crystal structure. This boron absorbs yellow light and reflects blue, giving the stone its unique and vivid appearance. Unlike other fancy colors created by distortion or defects, blue diamonds owe their color to actual elemental presence. These stones are geological miracles born in extreme environments, sometimes more than a billion years ago.
GIA 0.41 Carat Pear Diamond Fancy Intense Blue SI1 Clarity |

|
| Click on the Image |
Boron’s Role In Imparting The Blue Hue
Boron is a rare element in the Earth’s mantle, which is where diamonds form. For a diamond to turn blue, boron must replace nitrogen during crystal growth—an event that rarely happens. The boron atoms alter the diamond’s optical properties, creating the bluish tone. The more boron that gets embedded, the stronger the blue hue. Since boron presence is so limited in those high-pressure zones, naturally blue diamonds remain exceedingly scarce.
Blue Diamond vs. Colorless Diamond: Key Differences
Colorless diamonds are graded by how little color they contain. In contrast, fancy color diamonds like blue ones are valued for the depth and richness of their hue. Blue diamonds also tend to have a different chemical composition due to the boron, which affects their conductivity. In terms of pricing, even smaller blue diamonds often exceed the value of much larger white diamonds. Their rarity, formation process, and bold color make them a distinct category within the diamond market.
|
|
1.b) The Science Of Blue Diamond FormationBack To Top |
The formation of blue diamonds requires specific geological settings not found in most diamond-producing areas. These gems originate hundreds of kilometers below the Earth’s surface—far deeper than most other diamonds. As they rise, they carry clues about the planet’s deep interior and ancient activity.
Rare Geological Conditions In Earth’s Mantle
Blue diamonds form in parts of the Earth’s mantle rich in boron, which itself is scarce that deep. These zones lie beneath oceanic crust or ancient tectonic plates that were once submerged. Scientists believe boron reaches those depths through subduction—when seabed materials are pushed into the Earth. Because this process happens rarely and over immense time spans, blue diamond formation is incredibly infrequent.
Why Blue Diamonds Are Exceptionally Rare
The conditions needed to form a blue diamond align only under extraordinary circumstances. It’s not just about heat and pressure—there must also be the right trace elements at the right moment in geological time. That’s why even among fancy color diamonds, blue is considered ultra-rare. Tens of thousands of diamonds might be mined before one faint blue is found. Stronger colors like fancy vivid blue are even more uncommon.
GIA 0.74 Carat Radiant Diamond Fancy Intense Blue VS1 Clarity |

|
| Click on the Image |
How Blue Diamonds Are Brought To The Surface
Once formed, blue diamonds don’t simply sit near the surface. They’re carried upward by deep-source volcanic eruptions, specifically through kimberlite pipes. These violent eruptions are ancient and infrequent, which means the delivery of blue diamonds is both unpredictable and limited. That long journey—from extreme depths to auction houses and collectors’ vaults—adds to the diamond’s mystique and value.
|
|
2) Blue Diamond Color Grading And ClassificationBack To Top |
Color grading determines how valuable a blue diamond truly is. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) uses strict standards to assess color intensity. These grades help buyers, collectors, and investors compare different shades of natural blue diamonds accurately.
|
|
2.a) GIA Color Grades For Blue DiamondsBack To Top |
The GIA classifies blue diamonds based on hue, tone, and saturation. Their system includes nine distinct grades that describe how deep or vivid the blue appears. These grades significantly affect both pricing and demand.
From Faint Blue To Fancy Vivid Blue
Blue diamonds span a wide color range. GIA grades begin at Faint Blue, where the color is barely visible, and go up to Fancy Vivid Blue, which shows intense, striking saturation. As the grade increases, so does the price. Fancy Light Blue and Fancy Blue offer a soft yet noticeable hue. Fancy Intense and Fancy Vivid stand out with their richer and deeper blues. The vivid grade sits at the top, admired for its brightness and emotional pull. These diamonds often fetch record-breaking prices at auctions due to their extreme rarity.
Understanding Saturation, Tone, And Hue
Each blue diamond is evaluated for its hue (basic color), tone (lightness or darkness), and saturation (intensity of color). A well-balanced combination of medium tone and strong saturation is the sweet spot for collectors. Too light, and the diamond appears washed out. Too dark, and the sparkle can get lost. Saturation is the main value driver. Even if two diamonds look similar, the one with higher saturation will command a premium.
Why Fancy Vivid Blue Is The Most Prized Grade
Fancy Vivid Blue diamonds represent the highest color quality available in natural blue diamonds. Their saturation is rich and electric, with a tone that allows the stone to retain brilliance. Because they strike a perfect balance between depth and brightness, they attract global attention. These diamonds are extremely rare, and even small stones in this grade can reach seven-figure prices. They are the dream of every blue diamond enthusiast.
|
|
2.b) The Impact Of Secondary ColorsBack To Top |
Many blue diamonds show hints of other colors. These are known as modifiers or secondary hues. Their presence can either add visual interest or reduce the diamond’s value.
Grayish, Greenish, And Violetish Blue Tints
Secondary colors appear when other trace elements enter the diamond during formation. Grayish blue diamonds are quite common and tend to look steely or cool-toned. Greenish blue stones can appear slightly teal, offering a different personality. Rare violetish hues bring a slight purple cast. While beautiful, these modifiers change how the blue appears in natural light. Some collectors favor them, but most still seek a pure blue.
How Modifiers Affect A Diamond’s Value
Modifiers have a direct effect on pricing. Pure blue diamonds with no additional tints are the most expensive. If the secondary hue is desirable, like a soft violetish tone, it may have a neutral or mildly positive effect. But if the tint reduces color intensity or adds a dull cast, the value drops. In commercial terms, even a small difference in hue can mean thousands of dollars per carat.
GIA 0.31 Carat Round Diamond Fancy Blue VS2 Clarity |

|
| Click on the Image |
Pure Blue Color And Premium Pricing
A blue diamond with a pure, unmodified hue is incredibly rare. These stones exhibit a clean and powerful color that appears the same under various lighting conditions. Jewelers prize them for their visual purity. Investors pay top dollar because they hold value and rise quickly in price. In high-end auctions, pure fancy vivid blue diamonds often lead the event. Their unmatched rarity keeps them permanently in demand.
|
|
3) Natural Vs Treated And Synthetic Blue DiamondsBack To Top |
Not all blue diamonds are natural. Some are treated or created in labs. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right stone for your budget and purpose.
|
|
3.a) Natural Blue DiamondsBack To Top |
Natural blue diamonds are geological rarities. They form deep underground and owe their blue color to boron. These stones are the most valuable and sought-after in the diamond market.
Mined From Cullinan And Historic Golconda Sources
Some of the world’s most valuable blue diamonds come from just a handful of locations. The Cullinan Mine in South Africa continues to produce a limited number of natural blue diamonds each year. In the past, the Golconda region of India was a known source, producing legends like the Hope Diamond. These sources are either nearly exhausted or extremely limited, making each mined blue diamond a rare geological find.
Limited Annual Output From Global Mines
Only a few rough blue diamonds are discovered globally each year. Most are small and faint in color. The chance of finding a vivid or intense blue in large size is incredibly low. Even with modern mining technology, these diamonds appear unpredictably. That scarcity explains why natural blue diamonds remain among the most expensive gemstones in the world.
GIA 0.37 Carat Marquise Diamond 0.37ct Blue Color SI1 Clarity |
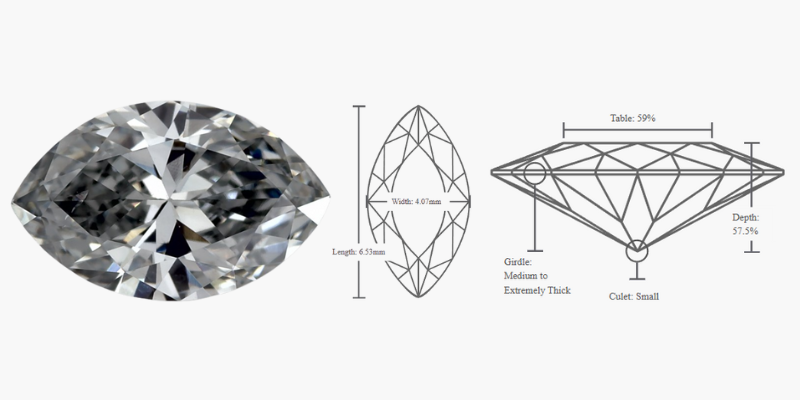
|
| Click on the Image |
Characteristics Of Naturally Formed Blue Diamonds
Natural blue diamonds show distinct color distribution and a soft, glowing saturation that synthetic or treated stones rarely match. Their hue results from boron trapped during formation, not artificial treatment. Many have a slight gray or green overtone, but the pure blues stand out. These diamonds are often accompanied by GIA certificates confirming natural origin and color, which boosts buyer confidence and value.
|
|
3.b) Treated And Irradiated Blue DiamondsBack To Top |
Some diamonds gain their color through artificial processes. These stones begin as colorless or brown diamonds and undergo treatment to create a blue hue. Treated diamonds offer a more affordable way to enjoy colored gems.
The Process Of Color Enhancement
Irradiation and high-temperature annealing are common methods used to turn low-value diamonds blue. These treatments change the atomic structure, allowing the diamond to absorb and reflect blue wavelengths. While they may look vibrant, these stones do not carry the same geological prestige or rarity as natural ones. Jewelers must disclose any such treatment.
How To Identify Treated Stones
Treated blue diamonds often show an unnaturally even or intense color that doesn’t shift under light. Specialized equipment can detect structural changes inside the stone. Reputable sellers always disclose if a diamond is color-enhanced. If you’re unsure, request a GIA or similar lab report before purchasing.
Why Treated Diamonds Cost Less
These diamonds are more affordable because their color isn’t naturally occurring. Although they can look stunning, collectors and investors usually prefer untreated stones. Treated diamonds don’t hold value the same way, and resale can be difficult. Still, they serve well for buyers who want the look without the premium price tag.
|
|
3.c) Lab-Grown Blue DiamondsBack To Top |
Lab-created blue diamonds mimic natural ones in chemical makeup. These stones are grown under controlled conditions and provide an ethical, eco-friendly option. As demand rises, lab diamonds continue to improve in quality and appearance.
How Lab Blue Diamonds Are Created
Scientists replicate the pressure and heat of the Earth’s mantle in a lab setting. By introducing boron during growth, they achieve a blue hue similar to that of natural stones. Methods like HPHT (High Pressure High Temperature) or CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) make this possible. The result is a real diamond, just without geological origin.
14K White Gold Twisting Split Shank Blue Diamond Center Halo Engagement Ring |

|
| Click on the Image |
Differences In Appearance And Price
At first glance, lab-grown blue diamonds may look nearly identical to natural ones. However, they often appear too perfect or clean under magnification. Price is the biggest difference—lab diamonds cost significantly less. For the same size and color grade, a lab stone can be up to 80% cheaper than a natural one.
Should You Consider Buying A Lab-Grown Blue Diamond?
If you’re focused on budget or ethical sourcing, lab diamonds are worth considering. They offer the same sparkle and durability as mined ones. Just remember, they won’t appreciate in value. For engagement rings or gifts, lab blue diamonds deliver visual impact at a fraction of the cost. For collectors or investors, though, natural stones remain the better long-term choice.
|
|
4) Where Do Blue Diamonds Come From?Back To Top |
Blue diamonds come from very few locations around the world. Their origins add to their rarity and mystique. Knowing where these stones are mined helps explain their high price and limited availability.
|
|
4.a) Famous Blue Diamond MinesBack To Top |
Only a handful of mines have produced natural blue diamonds. Some are still active today, while others are long depleted. Each mine has its own story and legacy in the diamond trade.
Cullinan Mine In South Africa
The Cullinan Mine is currently the most consistent source of natural blue diamonds. Located near Pretoria, South Africa, this mine has produced several famous blue stones, including pieces that later appeared in royal jewelry. The Cullinan Dream and Blue Moon Diamond both originated here. While production is low, the quality of color and size makes Cullinan a key player in the global blue diamond market.
Golconda Mines In India And The Hope Diamond
Centuries ago, the Golconda region in India produced some of history’s most legendary diamonds. These mines, located in present-day Telangana and Andhra Pradesh, were known for their large, flawless stones. The Hope Diamond, arguably the most famous blue diamond in existence, came from this region. Though no longer operational, Golconda’s impact on diamond history still echoes in auction rooms and museums around the world.
14k Gold Round-Cut Blue Diamond Halo Engagement Ring |

|
| Click on the Image |
Lesser-Known Sources Around The World
Apart from South Africa and India, a few other regions have yielded occasional blue diamonds. Australia’s Argyle Mine, better known for pinks, has reported rare blue finds. Some mines in Indonesia, Botswana, and even Brazil have also produced faint to light blue stones. These sources are inconsistent, and production is minimal, which reinforces how rare these gems truly are.
|
|
4.b) Historical Significance And Famous StonesBack To Top |
Blue diamonds have long captivated royalty, collectors, and gem enthusiasts. Their history includes mystery, fortune, and prestige. Many famous stones have changed hands across continents.
The Hope Diamond And Its Controversial Past
The Hope Diamond has a story that borders on myth. It began as the Tavernier Blue in 17th-century India and passed through French and British hands. After being stolen and recut during the French Revolution, it resurfaced as the Hope Diamond in England. Stories of misfortune and tragedy followed some of its owners, feeding its infamous reputation. Today, the 45.52-carat stone rests safely in the Smithsonian Museum, where it draws millions of visitors each year.
Other Legendary Blue Diamonds In History
Several other blue diamonds have made headlines over the decades. The Wittelsbach-Graff Diamond, a deep blue stone once part of Bavarian crown jewels, was recut and sold for millions. The Oppenheimer Blue set auction records, thanks to its size and saturation. Then there’s the Blue Moon of Josephine, a flawless vivid blue diamond that stunned the market with its sale price. These diamonds aren’t just stones—they’re symbols of wealth, power, and beauty.
Royal Collections And High-Profile Auctions
Many blue diamonds now sit in royal vaults or private collections. They appear occasionally at high-profile auctions where bidding wars break out among elite buyers. Sotheby’s and Christie’s have both featured record-breaking blue diamond sales. For collectors, owning such a gem is about prestige as much as investment. Every time a rare blue diamond hits the auction block, headlines follow, and values soar.
|
|
5) Blue Diamond Pricing And Value FactorsBack To Top |
Blue diamond prices are driven by rarity, color intensity, and demand from elite collectors and investors.
Understanding how pricing works helps you make smarter buying decisions, whether you’re investing or purchasing for personal wear.
|
|
5.a) What Makes Blue Diamonds So Expensive?Back To Top |
Several key factors drive up the price of blue diamonds—color saturation, natural origin, and stone clarity top the list.
The more vivid and pure the blue hue, the higher the diamond’s value on the open market.
Rarity, Size, Color Intensity, And Purity
Blue diamonds form under rare geological conditions, which makes their supply extremely limited. Those that display a strong, even blue color without visible inclusions are even harder to find. Large carat weights add another layer of scarcity—especially when combined with high clarity and vivid color grades like Fancy Intense or Fancy Vivid Blue. Each additional point of perfection pushes the price higher, especially if the stone is untreated and naturally formed.
18k Gold Cushion-Cut Blue Diamond Halo Engagement Ring |

|
| Click on the Image |
The Auction Factor: Record-Breaking Sales
Auction houses have a strong influence on how blue diamonds are priced. When you see a diamond like the Blue Moon or Oppenheimer Blue fetch tens of millions, it sets a benchmark that trickles down into the retail and private markets. These high-profile sales create a ripple effect. Collectors watch closely, and sellers often adjust their expectations based on past auction records, media buzz, and demand at the top end of the market.
Collector Demand And Limited Availability
Blue diamonds appeal to both luxury buyers and serious investors. Their rarity and visual impact make them trophy assets in private collections and museum vaults. Since global production remains low—just a fraction compared to white diamonds—the demand far outweighs the supply. When fewer new stones enter the market, existing ones appreciate faster, especially if they come with strong provenance or ideal gemological characteristics.
|
|
5.b) Price Per Carat And Market TrendsBack To Top |
Blue diamonds consistently lead the market in price per carat among all fancy color diamonds.
Studying recent data helps you spot trends and gauge long-term investment potential.
Blue Diamond Price Chart By Carat Weight
As a rule of thumb, price per carat jumps sharply as carat weight increases. A 0.5 carat Fancy Blue might cost under $100,000 per carat, while a 3-carat Fancy Vivid Blue can cross $1 million per carat. These figures aren’t random—they reflect the steep drop-off in supply at higher sizes and color intensities. Larger stones with vivid saturation are extremely rare, which is why even a small bump in weight can add hundreds of thousands to the final tag.
How Color Grade Influences Price
Color is the single most important factor in blue diamond pricing. The GIA color grading scale ranges from Faint Blue to Fancy Vivid Blue. Each step up adds a premium. For example, the difference between a Fancy Light and a Fancy Intense can be tens of thousands per carat. Pure hues command the highest rates. Once secondary tones like gray or green creep in, prices often adjust downward—even if clarity and size remain strong.
18k Gold Cushion-Cut Blue Diamond Halo Engagement Ring |

|
| Click on the Image |
Investment Value Over The Last 10 Years
Over the past decade, natural blue diamonds have consistently increased in value. While white diamonds have seen price fluctuations, blue stones—especially vivid ones—have shown steady growth. Auction data, private sales, and gem investment indexes all point in one direction: long-term appreciation. For investors, this makes them a serious asset class. For buyers, it offers confidence that their blue diamond likely won’t just sparkle—it’ll grow in worth too.
|
|
6) Blue Diamond Jewelry: Styles, Trends, And DemandBack To Top |
Blue diamond jewelry has taken center stage in high-end fashion and luxury markets. With its striking color and rarity, demand for blue diamond pieces continues to grow in 2025. From engagement rings to pendants, more buyers are now drawn to its bold and elegant look.
|
|
6.a) Blue Diamond Engagement RingsBack To Top |
Engagement rings featuring blue diamonds are gaining serious traction. Their rarity and symbolism make them stand out from traditional choices. You’ll find more designers embracing this trend for both men and women.
Why They’re Gaining Popularity In 2025
In 2025, people want jewelry that tells a personal story. Blue diamonds fit that desire. Their unique color represents trust, calm, and individuality—qualities couples admire in modern relationships. Celebrities and influencers have helped spark interest by showcasing blue diamond engagement rings in public appearances and social media. This added visibility has pushed the trend mainstream.
Men’s Blue Diamond Rings: A Rising Trend
Men are embracing diamonds more confidently now, and blue diamonds especially appeal due to their strong yet sophisticated vibe. The color blue connects with masculinity and power, making it a perfect fit for statement rings. Whether in bold signets or minimal bands, men’s blue diamond rings add flair without sacrificing subtlety. As fashion norms shift, you’ll likely see more men wearing blue diamond rings both casually and formally.
Setting Styles That Complement Blue Stones
The right setting can make or break a blue diamond’s visual impact. White gold and platinum help amplify the cool tone of the stone, while rose gold adds a warm contrast. Halo designs, filigree detailing, and vintage-inspired settings continue to dominate. For a clean, modern look, bezel and solitaire styles keep the focus on the stone’s vivid color. Jewelers often recommend settings that maximize light exposure to enhance brilliance.
|
|
6.b) Other Blue Diamond Jewelry PiecesBack To Top |
Beyond engagement rings, blue diamonds appear in a range of fine jewelry. Earrings, bracelets, and pendants showcase their versatility. These pieces offer both style and status.
Stud Earrings, Tennis Bracelets, And Pendants
Blue diamond stud earrings add a bold pop of color without being too flashy. Tennis bracelets with alternating white and blue diamonds create a sleek, balanced look. Pendants are also rising in popularity, especially when set with fancy vivid blue stones. These jewelry types appeal to both gift buyers and collectors who want wearable elegance. With the right lighting, blue diamonds in any format can outshine other gemstones in visual appeal.
Two-Tone Gold Settings And Custom Designs
Two-tone settings are a clever way to bring contrast and focus to blue diamonds. Combining white and yellow or rose gold highlights the stone’s hue while offering a unique design. Many buyers now opt for custom pieces to ensure their blue diamond jewelry feels one-of-a-kind. Jewelers are embracing this trend, offering custom craftsmanship that emphasizes personal style over mass production.
14K White Gold Twisting Infinity Gold and Blue Diamond Split Shank Pave Set Diamond Engagement Ring |

|
| Click on the Image To |
Matching Blue With Other Fancy Colored Diamonds
Pairing blue diamonds with other fancy colors—like pinks, canary yellows, or champagnes—creates stunning visual effects. These combinations work well in bracelets and multi-stone pendants. The contrast between cool and warm tones brings a modern twist to traditional styles. If you enjoy experimenting with color, mixing fancy colored diamonds allows you to wear something bold without being overpowering. It’s a rising trend among those who want more than just sparkle—they want personality.
|
|
7) How To Identify And Buy A Real Blue DiamondBack To Top |
Buying a real blue diamond takes more than just picking something that looks beautiful. You need to verify authenticity, natural origin, and clarity. Understanding these factors helps you make a confident, smart purchase.
|
|
7.a) Certifications And Lab ReportsBack To Top |
Every real blue diamond should come with proper documentation. Reputable sellers offer certification from trusted gem labs. These reports confirm color, clarity, cut, and origin.
GIA Certification For Fancy Color Diamonds
Always look for GIA certification when buying a natural blue diamond. The Gemological Institute of America sets the highest standards for grading fancy color diamonds. Their report details the origin of color, natural versus treated status, and precise grading for hue, tone, and saturation. This document gives you solid proof of what you’re paying for. Without it, you’re simply guessing.
Verifying Natural Origin And Color
To confirm you’re buying a genuine natural blue diamond, check the lab report carefully. Look for phrases like “Natural Color Origin” and “Not Treated.” These confirm the stone’s blue color formed naturally underground. Don’t rely on seller claims alone. Always ask to see the official grading report before agreeing to a purchase.
What VVS1, VVS2, And SI2 Mean In Blue Diamonds
Clarity grades like VVS1, VVS2, and SI2 refer to how many internal or external flaws a diamond has. VVS1 and VVS2 mean “Very Very Slightly Included,” while SI2 means “Slightly Included.” In colored diamonds, clarity still matters, but color is the main value factor. A Fancy Vivid Blue with SI2 clarity might still be worth more than a flawless white diamond. Understanding this balance helps you choose wisely.
|
|
7.b) Tips For Buyers And InvestorsBack To Top |
Whether you’re buying for love or investment, you need to shop smart. A few basic strategies can protect you from costly mistakes. Knowledge is your best tool.
Choose Reputable Jewelers Or Auction Houses
Buy only from trusted jewelers, established auction houses, or certified diamond dealers. Check their reviews, credentials, and history. Reputable sellers will always provide proper certification and answer every question clearly. Avoid sellers who refuse to show lab reports or pressure you into fast decisions.
Ask The Right Questions Before You Buy
Always ask if the diamond is natural or treated, what lab graded it, and whether the report matches the stone. Find out if the stone has secondary hues or visible inclusions. If you’re unsure about anything, get a second opinion. This isn’t just a purchase—it’s a major commitment, so take your time and ask every question that comes to mind.
Blue Diamond As A Long-Term Asset
Natural blue diamonds hold long-term value due to their rarity. They’re not just beautiful—they’re smart investments. Auction records continue to rise, especially for Fancy Vivid and Fancy Intense stones. If you’re thinking long-term, choose certified natural blue diamonds with strong color grades. They have a track record of appreciating in value while offering timeless beauty.
|
|
8) Most Famous Blue Diamonds In The WorldBack To Top |
Some blue diamonds have left permanent marks on history and culture. These legendary stones aren’t just valuable—they’re unforgettable. Their fame comes from rare size, deep color, and the fascinating stories tied to them.
|
|
8.a) The Hope DiamondBack To Top |
The Hope Diamond is the most recognized blue diamond in existence. Its history spans centuries, continents, and royal families. Even today, it draws curiosity and speculation.
History, Ownership, And Lore
The Hope Diamond began life as the Tavernier Blue, found in the Golconda mines of India. It passed through the hands of French and British royalty, was stolen during the French Revolution, and reappeared decades later in London. Over the years, myths surrounded it—some claimed it carried a curse that brought misfortune to its owners. The original Tavernier Blue was much larger and later cut down into the diamond we now know as the Hope Diamond. King Louis XIV officially owned the larger stone, which was recut and reduced after it was stolen from the French Crown Jewels. Whether fact or fiction, the legend only deepened public fascination.
Current Home At The Smithsonian
Today, the Hope Diamond rests safely at the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, D.C. It weighs 45.52 carats and displays a deep blue hue with a hint of gray. Visitors from around the world view it as one of the museum’s top attractions. The gem remains a centerpiece of the Smithsonian’s National Gem Collection and continues to inspire awe in everyone who sees it.
Why It Remains The Most Famous Blue Diamond
The Hope Diamond holds a rare combination of size, color, and mystery. Its deep, velvety blue sets it apart from every other blue diamond ever discovered. The historical journey—from Indian royalty to American museums—adds unmatched prestige. Add the whispered tales of curses and intrigue, and you get a diamond with both sparkle and suspense. No other stone stirs the imagination quite like this one.
|
|
8.b) Other Iconic Blue DiamondsBack To Top |
While the Hope Diamond is unmatched in fame, several other blue diamonds have made global headlines. These gems have achieved record prices and are often seen as symbols of elite taste.
The Wittelsbach-Graff Blue
The Wittelsbach-Graff Diamond weighs 31.06 carats and shows a fancy deep blue hue. Originally part of the Austrian and Bavarian crown jewels, it vanished for years before resurfacing in the 20th century. Laurence Graff acquired and recut the stone, improving clarity while sparking controversy among historians and gemologists. Some experts praised the recut for its enhanced brilliance, while others argued it damaged the diamond’s historical integrity. Despite the changes, it remains one of the most historically significant blue diamonds ever sold.
The Blue Moon Diamond
Discovered in South Africa, the Blue Moon Diamond weighs 12.03 carats and boasts a flawless fancy vivid blue color. In 2015, it sold for over $48 million, setting a new record price per carat at the time. Its name was inspired by the rare event of a “blue moon,” which matched the gem’s rarity. Today, it’s also known as the Blue Moon of Josephine after the buyer named it for his daughter. Since then, this diamond has retained the title of the most expensive blue diamond sold by price per carat, surpassing earlier records like the Oppenheimer Blue.
The Zoe Diamond And Oppenheimer Blue
The Zoe Diamond, a 9.75-carat vivid blue, fetched over $32 million at Sotheby’s, earning a record for its size and saturation. The Oppenheimer Blue, named after diamond dealer Philip Oppenheimer, weighed 14.62 carats and sold for $57.5 million. That sale briefly made it the most expensive blue diamond ever auctioned. While the record has since been surpassed, the Oppenheimer Blue still holds a place among the most iconic gems in auction history. Both stones highlight how collectors prize not just the stone, but the story and status it brings.
Or Learn About More Colored Diamonds As Follows:
See Also:
Fascinating Facts About Diamonds Straight From Tiffany & Co’s Chief Gemologist